
We are at WHX Labs Dubai 2026!
📅 10 – 13 February 2026
📌 Dubai, UAE
📍 Hall 4, Booth A.19
Join us at WHX Labs Dubai, part of the world's largest healthcare event!
At our booth, you’ll gain exclusive insights into the handling of the fastest standalone-system on the market, the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer, and discover exciting details about our EXIAS m|1 Electrolyte Module.
Our team is looking forward to meeting you in Dubai and sharing the latest innovations!
👉 For further event details, click here.
Venue:
Dubai World Trade Centre

We are at MEDICA 2025!
📅 17 – 20 November 2026
📌 Düsseldorf, Germany
📍 Hall 3, Booth F72-4
Join us at MEDICA 2025, the world’s leading medical trade fair!
At our booth, you’ll gain exclusive insights into the handling of the fastest standalone-system on the market, the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer, and discover exciting details about our EXIAS m|1 Electrolyte Module.
Our team is looking forward to meeting you in Düsseldorf and sharing the latest innovations!
👉 For further event details, click here.
Venue:
Messe Düsseldorf
Stockumer Kirchstraße 61
40474 Düsseldorf, Germany

Our First Veterinary Exhibition – ECVIM-CA 2025 in Maastricht
With the EXIAS e|1vet, we are bringing the gold standard from human diagnostics into the world of veterinary medicine. Visit us from September 18–20 at ECVIM-CA in Maastricht and experience our maintenance-free, precise, and fast electrolyte analyzer designed for veterinary use.
Stop by our booth No. 15 in the Expo Foyer – #TeamEXIAS is looking forward to seeing you!
For more details about the event, please click here.
MECC Maastricht
Forum 100
6229 GV Maastricht, Netherland
Scientific Abstract
Schlaminger¹, B. Webb², A. Bartel², T. Niedrist³, M. Herrmann³, H. Scharnagl³
1 EXIAS Medical GmbH, Graz, Austria
2 MEON Medical Solutions GmbH & Co KG, Graz, Austria
3 Clinical Institute of Medical and Chemical Laboratory Diagnostics, Medical University of Graz, Austria
BACKGROUND/AIM
Accurate electrolyte measurement is critical for diagnosing and managing disorders of fluid and electrolyte balance. This study evaluates the effect of plasma protein levels on sodium (Na), potassium (K), and chloride (Cl) measurements using direct and indirect ion-selective electrode (ISE) methods, focusing on protein-induced matrix effects such as pseudohypernatremia and pseudohyponatremia. These phenomena occur because indirect ISE methods measure ion activity in a diluted sample, requiring mathematical correction based on assumptions about plasma water content that may not hold in abnormal protein states [1]. Previous research demonstrated that up to 25% of samples from critically ill patients could be misclassified when using indirect ISE methods in cases of abnormal protein concentrations [1] [2], of which 97% occur in hypoproteinemic samples [2].
METHODS
In leftover plasma samples (n=120, Li Hep), electrolyte (Na, K, Cl) concentrations were measured on the solite analyzer (MEON Medical Solutions) with integrated m|1 electrolyte module (EXIAS Medical) as well as on the Cobas 8000 analyzer (Roche Diagnostics). The m|1 electrolyte module uses direct ISE, while the Cobas 8000 uses indirect ISE. Additionally, total protein (TP) concentrations were determined for the same samples on the Cobas 8000.
Samples were classified into hypoproteinemic (<6.6 g/dL; 64.4%) and normoproteinemic (6.6–8.7 g/dL; 35.6%) groups based on TP levels. Systematic biases between methods were assessed using Bland-Altman analysis and linear regression modelling. A multifactorial linear model incorporating electrolyte concentration (Na, K, Cl), TP levels, and an intercept was used to quantify the impact of protein levels on electrolyte measurements.
RESULTS
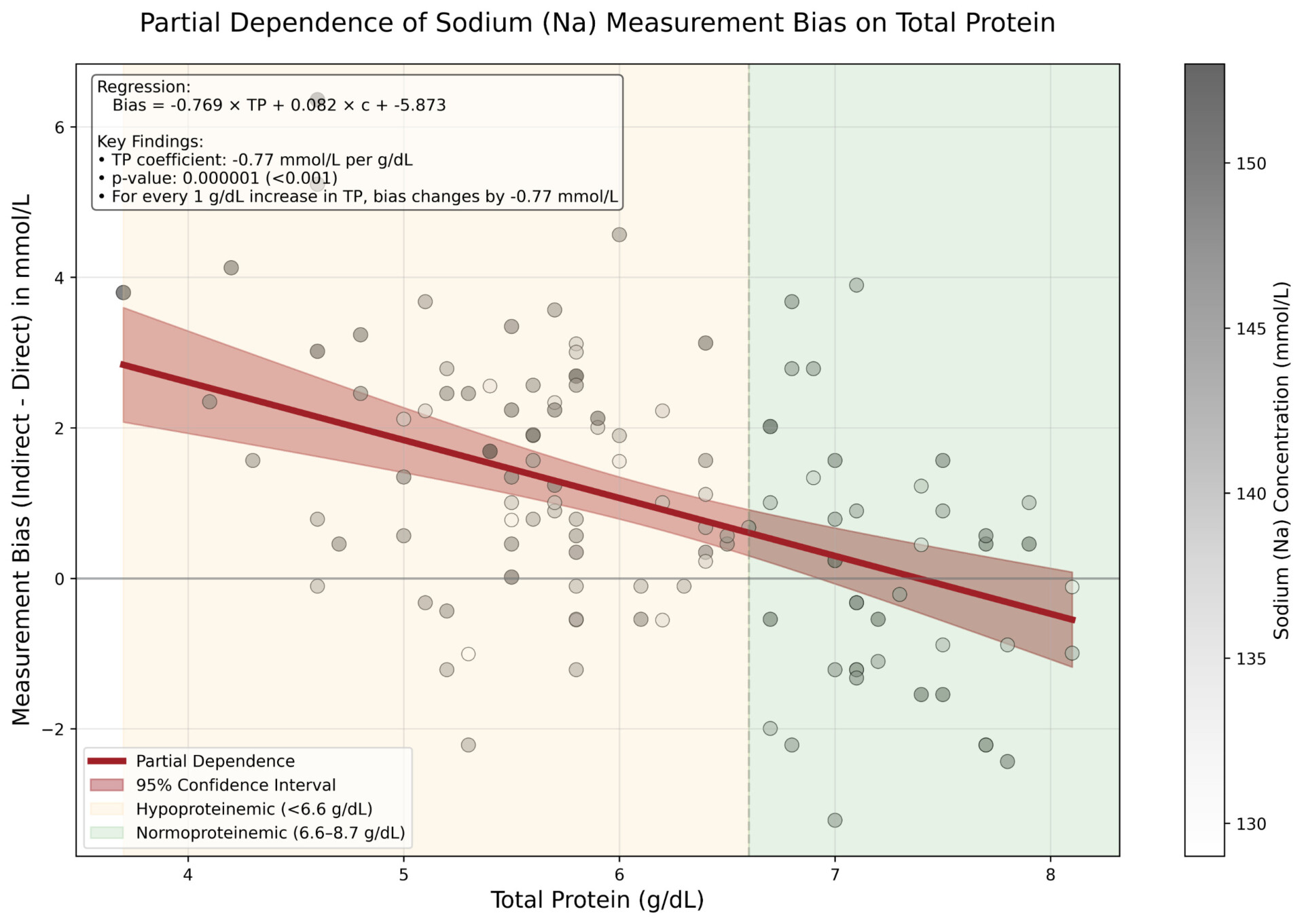
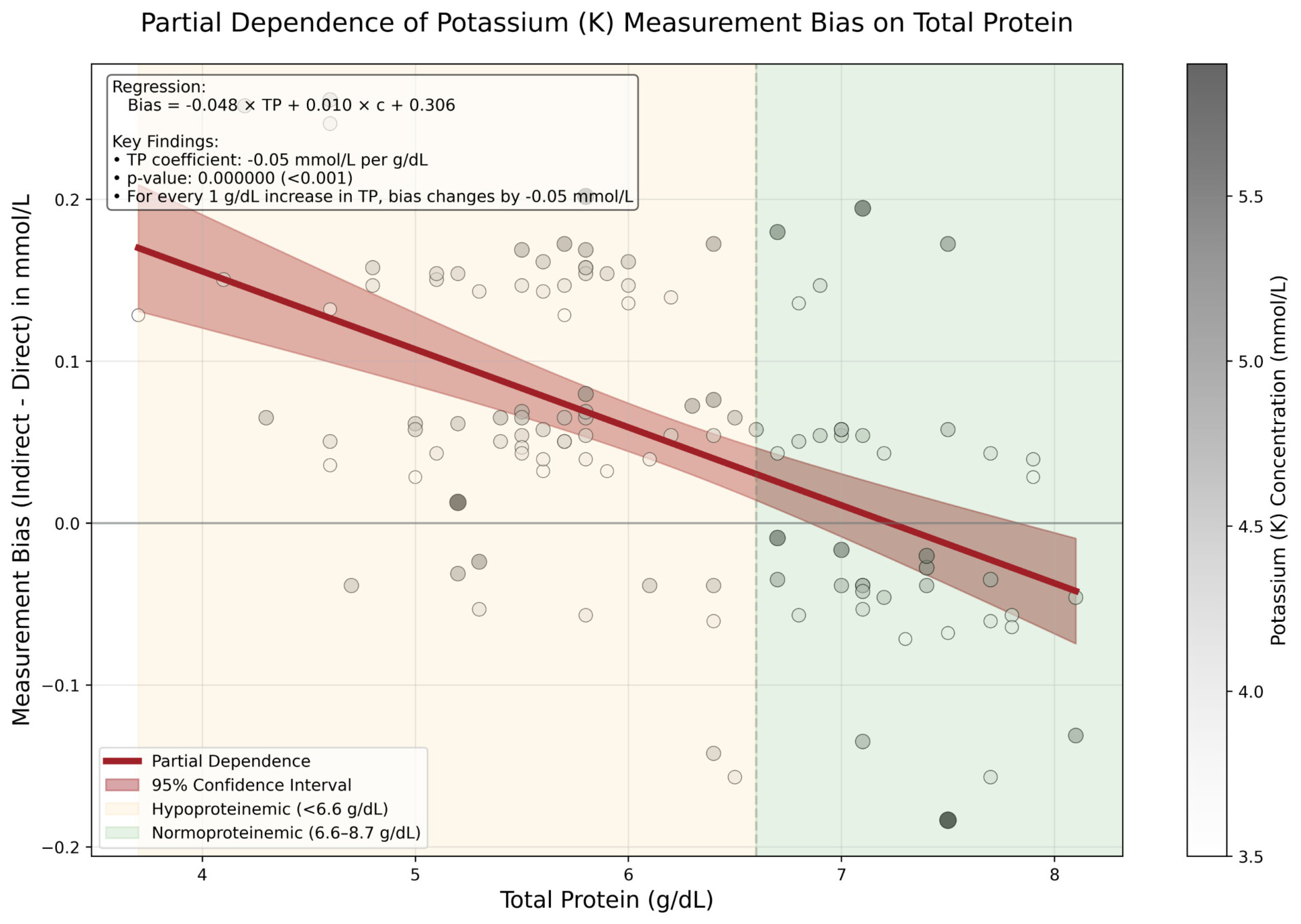
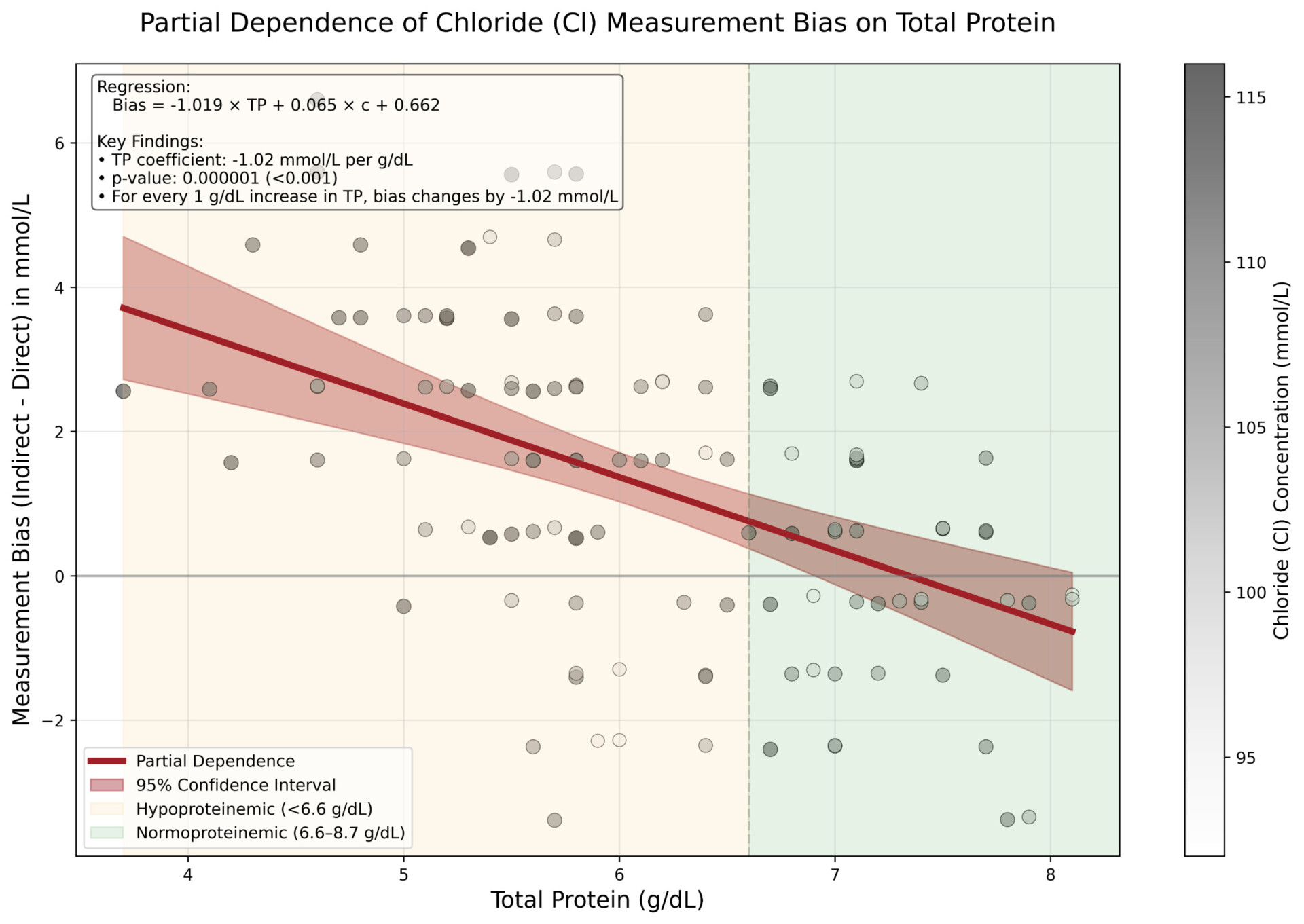
Significant biases (p < 0.05) were observed across all electrolytes. For every 1 g/dL increase in TP, indirect ISE underestimated Na by 0.77 mmol/L (p < 0.001), K by 0.05 mmol/L (p < 0.001) and Cl by 1.02 mmol/L (p < 0.001) compared to direct ISE. Hence, indirect ISE overestimates Na levels (e.g., pseudohypernatremia) in hypoproteinemic specimens and underestimates Na levels (e.g., pseudohyponatremia) in hyperproteinemic specimens [3].
These observed biases closely matched theoretical expectations based on plasma water fraction changes with varying protein concentrations [4]. Correcting for systematic differences confirmed that biases were exclusively attributable to TP levels.
Notably, our dataset did not include hyperproteinemic samples (>8.7 g/dL), limiting our direct observations to hypoproteinemic and normoproteinemic ranges.
Conclusion
Direct ISE methods provide more accurate measurements of Na, K, and Cl across varying protein levels (3.7 – 8.1 g/dL) compared to indirect ISE methods, which are prone to protein-induced matrix effects due to their dilution step and the compensation applied to account for it. The magnitude of this effect is clinically significant, particularly for sodium measurements in critically ill patients who are often present with abnormal protein levels.
Our results confirm and extend earlier observations by Dimeski et al. [1],[2], highlighting that the risk of misclassification is substantial and directly proportional to the deviation from normal protein levels. The observed coefficient of -0.77 mmol/L per g/dL for sodium aligns well with previous estimates (-0.78 to -0.98 mmol/L per g/dL) [2], supporting the consistency of this phenomenon across different analytical platforms.
These findings align with recent consensus recommendations suggesting direct ISE methods should be preferred [5]. Selecting appropriate measurement techniques is critical in clinical settings to minimize errors in electrolyte assessment caused by plasma protein variations. [5], [6]
References:
[1] Dimeski G, Barnett RJ. Effects of total plasma protein concentration on plasma sodium, potassium and chloride measurements by an indirect ion selective electrode measuring system. Crit Care Resusc. 2005;7(1):12-15.
[2] Dimeski G, Morgan TJ, Presneill JJ, Venkatesh B. Disagreement between ion selective electrode direct and indirect sodium measurements: estimation of the problem in a tertiary referral hospital. J Crit Care. 2012;27(3):326.e9-16.
[3] Liamis G, Liberopoulos E, Barkas F, Elisaf M. Spurious electrolyte disorders: a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Am J Nephrol. 2013;38(1):50-57.
[4] Nguyen MK, Ornekian V, Butch AW, Kurtz I. A new method for determining plasma water content: application in pseudohyponatremia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(5)
[5] Langelaan ML, Kamp L, Zandijk E, Raijmakers MT. Prevalence of pseudonatremia in a clinical laboratory - role of the water content. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017 Mar 1;55(4):546-553
[6] King RI, Mackay RJ, Florkowski CM, Lynn AM. Electrolytes in sick neonates - which sodium is the right answer? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013;98(1)

Visit us in Brussels, Belgium from 18th till 22nd May 2025!
At booth #276 you are going to get exclusive insights into the handling of the fastest standalone-system on the market, the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer and receive interesting details about our EXIAS m|1 Electrolyte Module.
Our Team awaits you at the EUROMEDLAB Brussels 2025!
For further event details click here.
BRUXELLES EXPO
Place de Belgique 1
1020 Brussels, Belgium

EXPERIENCE THE NEXT GENERATION OF ELECTROLYTE ANALYZERS AND MEET THE TEAM IN DUBAI
Visit us at Booth F38, Hall Z6, from February 3-6, 2025. Our team will be on hand to demonstrate the capabilities of the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer, featuring its maintenance-free design, minimal sample volume, and on-board QC option.
We are looking forward to meeting you!
More event details: https://www.medlabme.com/en/home.html
Dubai World Trade Centre
Dubai, UAE
United Arab Emirates
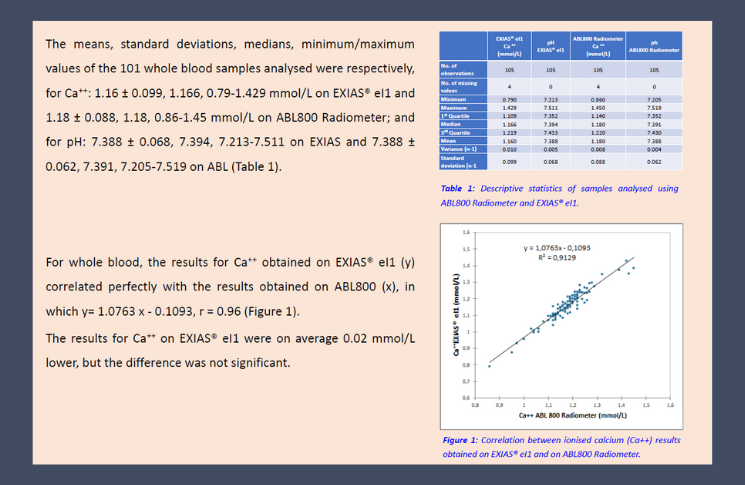
EXIAS is excited to announce the results of two recent comparative studies conducted by the Biochemistry Laboratory of the University of Nantes. These studies evaluated the analytical performance of the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer against other automated laboratory systems, focusing on key parameters such as electrolytes (sodium and potassium) and ionized calcium.
The findings of these studies highlight that the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer delivers precision and reliability comparable to some of the best-in-class devices on the market. In one study, the electrolytes (Na+, K+) measured using the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer demonstrated excellent accuracy when compared to other automated systems. In a separate study, the performance of the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer in measuring ionized calcium was directly compared with the Radiometer ABL800, further proving its exceptional analytical capabilities.
These results confirm the EXIAS e|1 Analyzer's position as a high-quality solution for reliable and precise testing – in the laboratory as well as in point-of-care environment. We are proud to share these achievements, reflecting our ongoing commitment to providing top-tier analytical performance.
For more details, please find the full posters released in June 2024.

In response to substantial feedback and high demand, EXIAS has introduced new Cartridge versions for the e|1 Analyzer to enhance flexibility for laboratories and point-of-care environments of all sizes.
The newly launched Cartridge 100 is capable of performing 100 tests within an in-use time of 42 days. Additionally, the in-use time of the existing Cartridge 600 has been extended from 28 to 42 days. This makes it the perfect choice for a much broader user segment. Furthermore, both Cartridge versions are available with optional on-board Quality Control.
These advancements mark an extension of the EXIAS product portfolio, providing especially end-users with more options and greater convenience. This improvement is particularly beneficial for both low and middle-to-high sample throughput segments: For laboratories and facilities conducting a few tests per week, as well as those performing around 100 tests per week, the e|1 Analyzer now presents an even more compelling choice.
The new Cartridges are available in all countries where the necessary registrations have been completed. This strategic enhancement is expected to solidify EXIAS's position in the market, demonstrating their commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.

EXPERIENCE THE NEXT GENERATION OF ELECTROLYTE ANALYZERS AND MEET THE TEAM IN DÜSSELDORF, GERMANY
Stop by November 11-14, 2024 at our booth F72-3 in hall 3 to meet the team and discover the EXIAS in vitro diagnostic solutions.
The truly maintenance-free EXIAS e|1 Analyzer is cartridge-based, uses very low sample volume, measures in only 25 seconds, and it offers optional on-board quality control. We are inviting you to join our booth and learn more.
We are looking forward to meeting you!
More event details: https://www.medica-tradefair.com/
Messe Düsseldorf
Stockumer Kirchstraße 61
40474 Düsseldorf
Germany

EXPERIENCE THE NEXT GENERATION OF ELECTROLYTE ANALYZERS AND MEET THE TEAM IN BANGKOK, THAILAND.
Stop by from July 10-12, 2024 at our booth no. H6 F31 to meet the team and discover the EXIAS in vitro diagnostic solutions. The truly maintenance-free EXIAS e|1 Analyzer is cartridge-based, uses very low sample volume, measures in only 25 seconds, and it offers optional on-board quality control. We are inviting you to join our booth and learn more.
We are looking forward to meeting you!
